Vector Corner Pin
![]()
Brief Description
This modifier is very similar to the UV Map Generator: It internally generate UV Maps using a motion-vector pass analysis and applies it to the source image. Moreover, the vectors also used to drive a Corner Pin so that it is possible to set keyframes if the vectors make the source image drift too much. The motion vectors influence parameter can control the influence of the motion vectors against the Corner Pin to prevent the vectors from drifting locally too much.
Description
The Vector Corner Pin modifier is very similar to the UV Map generator and shares the same workflow.
In order to place the image to match-move correctly, the Vector Corner Pin offers a Corner Pin widget right in the viewport on which you can move the To Points.
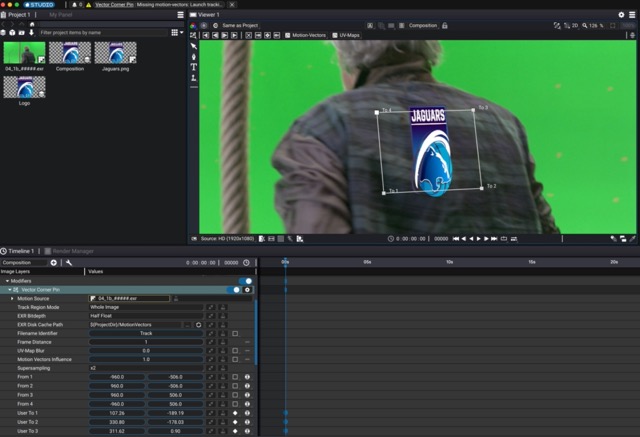
Whenever moving the To Points, a keyframe will be created on the "User To" parameters in the timeline. Each keyframe serves as a new reference frame for the UV maps: at a keyframe, the deformation caused by the UV Map will be pass-through and only the Corner Pin you adjust is used as transformation on the image.
Whenever adding new keyframes or editing keyframes, you need to re-track the UV-Maps in between the previous and next keyframes. To do so, you can use the horizontal toolbar in the viewer contextual interface.
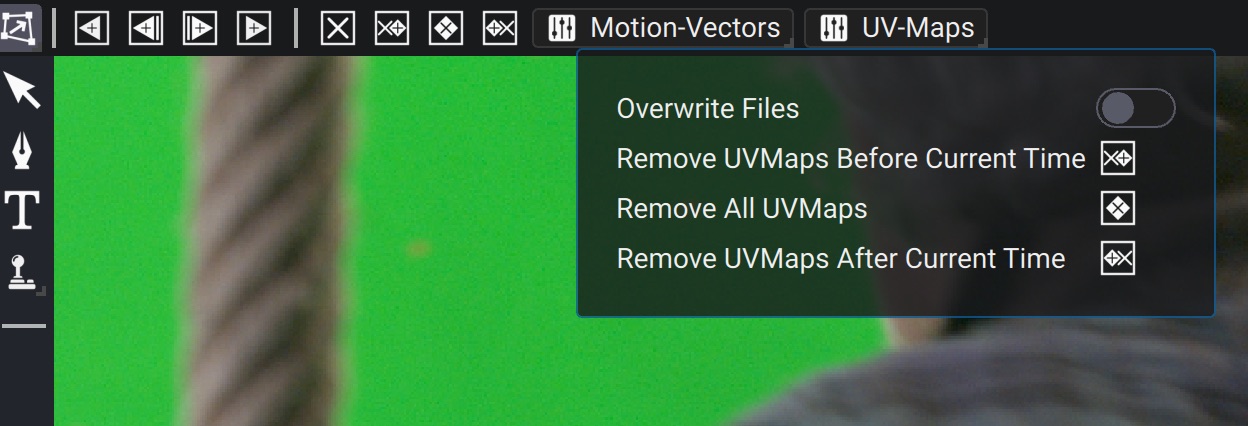
The first 4 buttons are used to launch tracking over different ranges of frames. The next 4 buttons are used to remove keyframes on the Corner Pin. The Motion-Vectors and UV-Maps menus are useful to remove generated files on disk.
When Overwrite Files is left unchecked in the menu, any existing file will be preserved when re-generating, thus skipping computations. Turning it on will force a re-generation of the motion-vectors/UV-Maps.
Changing these parameters require a recomputation of the motion-vectors:
- Frame Distance
- Motion Estimation parameters
- EXR Disk Cache Path
- Filename Identifier
- Track Region Mode or Track Region rectangle
- Motion source
Changing these parameters require a recomputation of the UV-Maps:
- Any parameters that affect the motion-vectors
- Any change made on the Corner Pin
Setting new keyframes
When the match-move starts to drift, you can place a new keyframe by moving any To point in the viewport. You will then need to relaunch a track, using the viewer toolbar. Make sure "Overwrite Files" in the UV-Maps settings is checked.
Smoothing the motion
You may want to reduce the strength of the deformation caused by the motion vectors. To do so, the following parameters can be used:
-
Frame Distance: Increase it to compute vectors across a longer range of time so that motion is more smooth. For fast motions, this can lead to drifts
-
UV-Map Blur: Slightly blur the map in order to avoid artefacts. A high blur can lead to drift in areas with complexe motions, such as the border of the lips of a human face
-
Motion-Vectors influence: Reducing it will give more weight to the Corner Pin transformation, reducing the visible deformation applied by the motion vectors.
Controls
| Parameter / Script Name | Type | Default | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
Enabled / enabled | Boolean | On | |
Motion Estimation / motionEstimation | Category | - | |
Motion Source / motionSource | Image | - | The footage that will be used to compute the motion-vectors |
Track Region / roi | -200, -200, 200, 200 | Only pixels within this region will be tracked. This is useful for example if you need to track a small portion of the image. Note that the rectangle should be large enough to enclose all possible position of the pixels throughout the track length | |
Track Region Mode / roiMode | Choice | Whole Image | The region used to track the pixels. Selecting Track Region and defining a smaller rectangle may improve performances - Track Region - Whole Image |
EXR Disk Cache Path / cache_path | File | Path where computed motion vectors and UVMaps are stored. The ${ProjectDir} variable can be used to refer to the directory where the project file is located. If the project is not yet saved, the vectors are stored in a temporary location on your system | |
Filename Identifier / uv_basename | UV-maps and motion vectors files will be named on disk as following with: "uv_" or "mv_", followed by this identifier and ending with informations such as frame distance, reference frame and frame numbering | ||
Frame Distance / frame_distance | Float | 1 | Number of separating frames between a frame and the next when computing motion vectors. A higher value will smooth out jitter. It affects the tracking of motion-vectors and UV-Maps |
Use GPU If Available / use_gpu | Boolean | Off | Use CUDA for motion-vectors computation if possible. Results may differ slightly from CPU version and depending on the CUDA driver. It is safer to leave it disabled. |
UV-Map Blur / blur | Float | 0 | Smooth the UV-Map as a post-process before applying the UVs. It does not affect the tracking process |
Track Red / track_red | Boolean | On | Consider the source image red channel when tracking |
Track Green / track_green | Boolean | On | Consider the source image green channel when tracking |
Track Blue / track_blue | Boolean | On | Consider the source image blue channel when tracking |
Motion Vectors Influence / mv_influence_multiplier | Float | 1 | Motion vectors are most influent when between keyframes on the User To points. To reduce strength of the motion vectors, decrease this value. It does not affect the tracking process. |
Supersampling / supersampling | Choice | x2 | The supersampling factor. Higher means more quality and antialiasing but slower to render - x1 - x2 - x4 - x8 - x16 |
Filter / filter | Choice | Inherit | The antialiasing algorithm used as reconstruction filter. Note that if the uv map contains offset where 2 source pixels do not end up close-by in the output image, any reconstruction filter would produce incorrect results by mixing pixels that are apart in the source image. The only correct way to antialias in this mode is using a supersampling factor below and set filter to Nearest - Inherit: Inherit parent layer filter - None: No interpolation - Box: Box filter - Triangle: Bilinear filter - Hermite: Hermite interpolation filter (smoothstep in glsl) - Hann - Hamming - Blackman - Gaussian - Quadratic - Cubic: General Cubic Filter. Emulates a Gaussian Blurring Filter. This curve is also known as a 'B-Spline' interpolation curve, and is also commonly used for drawing smooth lines through a collection of points. It is also often used for camera and object motions in animations, to produce a smooth flow though the user provided control point - Spline 16 - Spline 36 - Spline 64 - Spline 100 - Spline 144 - Catmull-Rom - Mitchell - Keys - Keys Sharp - Sinc - Jinc - Kaiser - Welch - Parzen - Bohman - Cosine - Bartlett - Lagrange 3 - Lanczos 2 - Lanczos 2 Sharp - Lanczos 3 - Lanczos 3 Sharp - Lanczos 4 - Lanczos 6 |
From 1 / from_bl | Float 2D | 0, 0 | |
From 2 / from_br | Float 2D | 0, 0 | |
From 3 / from_tr | Float 2D | 0, 0 | |
From 4 / from_tl | Float 2D | 0, 0 | |
User To 1 / to_bl | Float 2D | 0, 0 | |
User To 2 / to_br | Float 2D | 0, 0 | |
User To 3 / to_tr | Float 2D | 0, 0 | |
User To 4 / to_tl | Float 2D | 0, 0 | |
Track To 1 / mvToBL | Float 2D | 0, 0 | |
Track To 2 / mvToBR | Float 2D | 0, 0 | |
Track To 3 / mvToTR | Float 2D | 0, 0 | |
Track To 4 / mvToTL | Float 2D | 0, 0 | |
Algorithm / of_algo | Choice | Dense Inverse Search | - Dense Inverse Search - Dual TV L1 |
Finest Scale / of_dis_finest_scale | Float | 1 | The finest level of the Gaussian pyramid on which the flow is computed (zero level corresponds to the original image resolution). The final flow is obtained by bilinear upscaling. |
Patch Size / of_dis_patch_size | Float | 8 | Size of an image patch for matching (in pixels). Normally, default 8x8 patches work well enough in most cases. |
Patch Stride / of_dis_patch_stride | Float | 3 | Stride between neighbor patches. Must be less than patch size. Lower values correspond to higher flow quality. |
Descent Num. Iterations / of_dis_gradient_descent_iters | Float | 25 | Maximum number of gradient descent iterations in the patch inverse search stage. Higher values may improve quality in some cases. |
Refinement Num. Iterations / of_dis_var_refinement_iters | Float | 5 | Number of fixed point iterations of variational refinement per scale. Set to zero to disable variational refinement completely. Higher values will typically result in more smooth and high-quality flow. |
Refinement Smoothness Weight / of_dis_var_refinement_alpha | Float | 20 | Weight of the smoothness term |
Refinement Gradient Constancy / of_dis_var_refinement_gamma | Float | 10 | Weight of the gradient constancy term |
Refinement Color Constancy / of_dis_var_refinement_delta | Float | 5 | Weight of the color constancy term |
Robust To Illumination Changes / of_dis_use_mean_propagation | Boolean | On | Whether to use mean-normalization of patches when computing patch distance. It is turned on by default as it typically provides a noticeable quality boost because of increased robustness to illumination variations. Turn it off if you are certain that your sequence doesn't contain any changes in illumination. |
Spatial Propagation / of_dis_use_spatial_propagation | Boolean | On | Whether to use spatial propagation of good optical flow vectors. This option is turned on by default, as it tends to work better on average and can sometimes help recover from major errors introduced by the coarse-to-fine scheme employed. Turning this option off can make the output flow field a bit smoother |
Time Step (Tau) / of_dualtvl1_tau | Float | 0.25 | Time step of the numerical scheme |
Attachment Weight / of_dualtvl1_lambda | Float | 0.15 | Weight parameter for the data term, attachment parameter. This is the most relevant parameter, which determines the smoothness of the output. The smaller this parameter is, the smoother the solutions we obtain. It depends on the range of motions of the images, so its value should be adapted to each image sequence. |
Tightness Weight / of_dualtvl1_theta | Float | 0.15 | Link between the attachment and the regularization terms. In theory, it should have a small value in order to maintain both parts in correspondence. The method is stable for a large range of values of this parameter. |
Pyramide Size / of_dualtvl1_nscales | Float | 5 | Number of scales used to create the pyramid of images |
Num. Warps / of_dualtvl1_warps | Float | 5 | Number of warpings per scale. This ensures the stability of the method. The higher it is, the more accurate it is, but slower |
Error Tolerance / of_dualtvl1_epsilon | Float | 0.01 | Stopping criterion threshold used in the numerical scheme, which is a trade-off between precision and running time. A small value will yield more accurate solutions at the expense of a slower convergence. |
Inner Iterations / of_dualtvl1_inner_iter | Float | 30 | Iterations number used when filtering outliers |
Outer Iterations / of_dualtvl1_outter_iter | Float | 10 | Number of iterations used in the numerical scheme |
Scale Step / of_dualtvl1_scale_step | Float | 0.8 | Step between pyramid scales |
Median Filter Size / of_dualtvl1_median_filter_size | Float | 5 | Size of the median filter kernel (1 = no filter). Must be 1, 3 or 5 |